Dietary supplements come in many forms, from vitamins and minerals to herbs, probiotics, amino acids, enzymes, and more. The most common types are multivitamins and single-nutrient supplements. Multivitamins offer a blend of essential nutrients in balanced proportions, while single-nutrient supplements provide concentrated doses of specific vitamins, minerals, or compounds.
Understanding the key differences between these two supplement types allows you to make more informed choices, and best support your needs as they change over time (due to diet, lifestyle, health conditions, age, and medications).
Understand the Difference
While both multivitamins and single-nutrient supplements support well-being, they do so differently.
Multivitamins help provide the consumer with an excellent nutritional foundation to support overall good health. They are formulated to help meet recommended dietary intakes and prevent nutrient deficiencies. It usually contains a combination of essential vitamins and minerals and most multivitamins provide these basic ingredients:
- Vitamins: A, C, D, E, K, B vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, folate, biotin, etc.)
- Minerals: calcium, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, manganese, chromium, etc.
- Other common additions: omega-3s, probiotics, antioxidants, plant extracts, amino acids.
Premium quality formulas may contain additional co-factors and natural ingredients to support the bioavailability of the products as a whole which ensures maximum delivery and absorption. For example, we include piperine (derived from black pepper) in our multivitamin formulas to support the absorption of many nutrients in the digestive tract.
Single nutrient supplements on the other hand allow the consumer to customize their regimen to their specific needs. They provide concentrated amounts of individual vitamins, minerals, or other natural substances like omega-3 fatty acids, or pro and prebiotics.
The higher, and therapeutic doses of key ingredients allow for more targeted needs with specific health concerns or goals in mind. Single nutrient supplements can be beneficial in certain situations, such as ashwagandha for stress, or vitamin B12 for vegans.
Some examples of widely used single-nutrient supplements include:
- CoQ10 – aging and heart health support.
- Vitamin D - immune system support.
- Calcium - bone health support.
- Omega-3s - heart, brain, and joint health.
Single-nutrient supplements may also require additional supporting ingredient(s) to enhance their quality and efficacy. Hence you may find that Xtendlife single-nutrient supplements may still contain more than one ingredient. For example, our CoQ10 products (Omega 3 / QH Premium CoQ10 and Xtend-Quinol) both contain quality ubiquinol CoQ10. Fish Oil Fatty Acids and Geranylgeraniol (GG) help the body to achieve the best absorption of CoQ10.
Do I Need a Multivitamin?
Most likely. Unfortunately, our modern diet has evolved, and it's becoming increasingly difficult to obtain all essential daily nutrients solely from our food intake. Fresh foods are no longer as nutrient-rich as they once were, and modern food production processes often lead to nutrient loss. Pre-prepared, pre-packaged, and processed foods tend to lack essential vitamins and minerals. Therefore, supplementing with a quality multivitamin is beneficial for most individuals, even those who consume a healthy whole-food diet. Additionally, children and older adults can particularly benefit from multivitamins to ensure they meet their age-specific nutrient needs.
However, if there's a specific nutrient deficiency, selecting individual nutrients in higher quantities can address deficiencies and provide immediate support, especially for those with restrictive diets such as vegans. Nonetheless, sometimes a combination with a multivitamin is optimal.
So, which supplement should you choose? The key factors to consider include:
- Do you aim to support overall health and well-being?
- If yes, consider multivitamins.
- If no, see the question below.
- Do you have specific health concerns or goals that you seek to address with supplementation?
- If yes, opt for one or more single-ingredient supplements.
Don’t forget! It is important to re-evaluate your supplement regimen periodically. As we age or our health concerns evolve, it's essential to evaluate our supplementation goals to ensure we're taking the most suitable supplements for our needs.
Further Important Aspects to Consider
Doctor's Recommendations
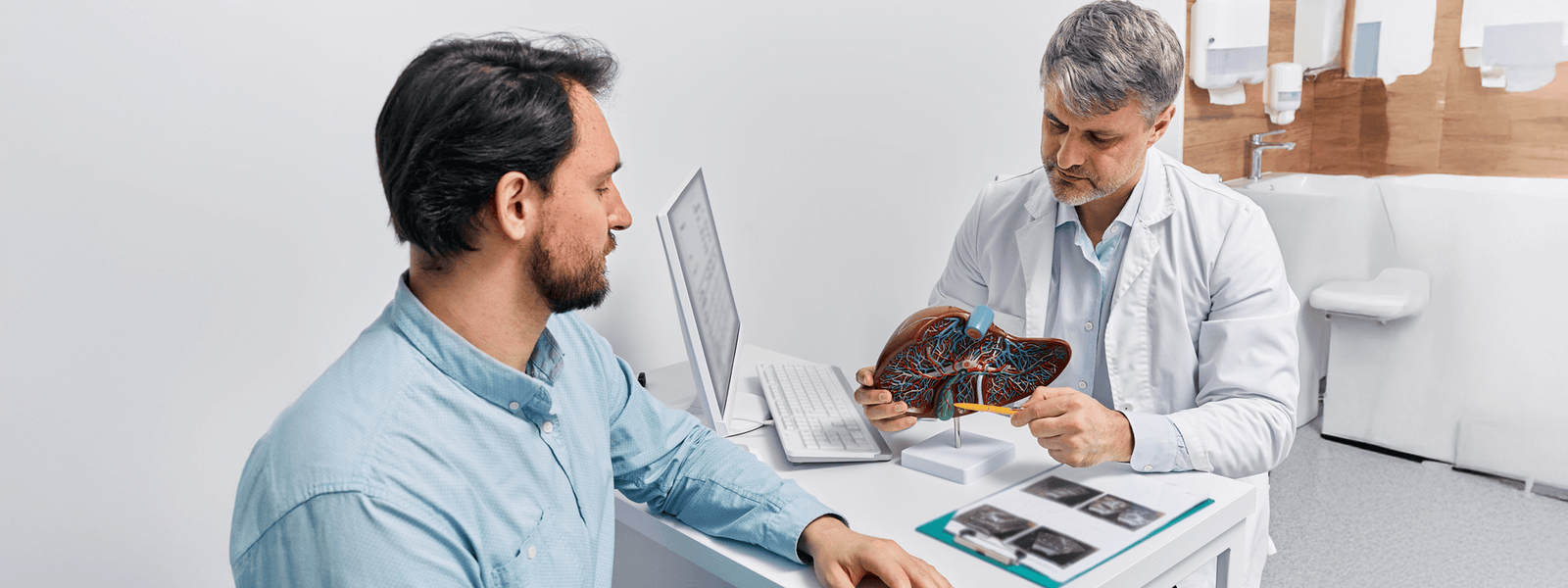
Before taking any new natural supplement, consult your physician, especially if managing a health condition. Negative interactions can occur between some common ingredients found in supplements and prescription medications. Also, we recommend leaving a gap of at least 2 hours between taking prescription medications and natural supplements. Additionally, nutrient deficiencies are best diagnosed by medical testing, after which appropriate supplementation can be advised. Ongoing oversight by a medical professional may be required to ensure that supplementation is still required.
Quality and Formulation of the Supplement
Carefully assess any supplement you are considering purchasing; this includes the manufacturer that produced the product. Check the supplement's ingredients information for the specific form of the ingredients used. Are they a bioavailable form? Also, does the daily dose meet my needs, and are there any other additional ingredients?
Be sure to check out the manufacturer's website for information on production facility certifications from internationally recognized authorities, quality control practices, supporting evidence of product and ingredient efficacy, and company ethics and business goals.


 Supplements
Supplements Superfoods
Superfoods Bundles
Bundles